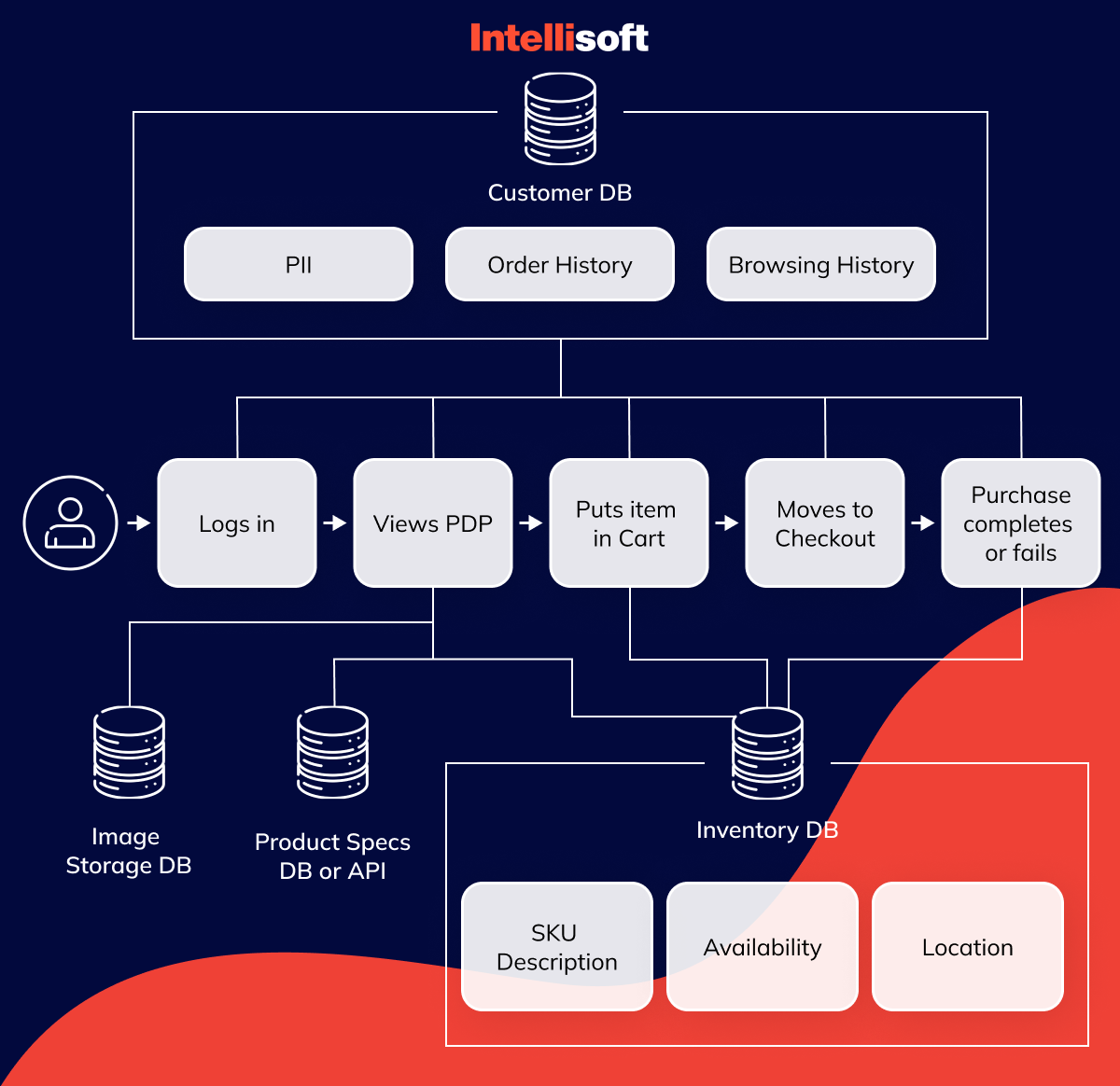
Creating inventory management software in Python can streamline your business operations. With Python’s versatility, you can develop a tool tailored to your specific needs.
Inventory management is crucial for any business, ensuring you have the right products at the right time. Python, a powerful and user-friendly programming language, offers the perfect platform to build such a tool. This guide will walk you through the steps needed to create effective inventory management software using Python. By the end, you’ll have a functional program to help you manage stock, track products, and optimize your inventory processes. Let’s dive in and start coding your custom solution. For more effective project management, consider using TidyCal for scheduling your development tasks. Check it out here.
Credit: intellisoft.io
Introduction To Inventory Management Software
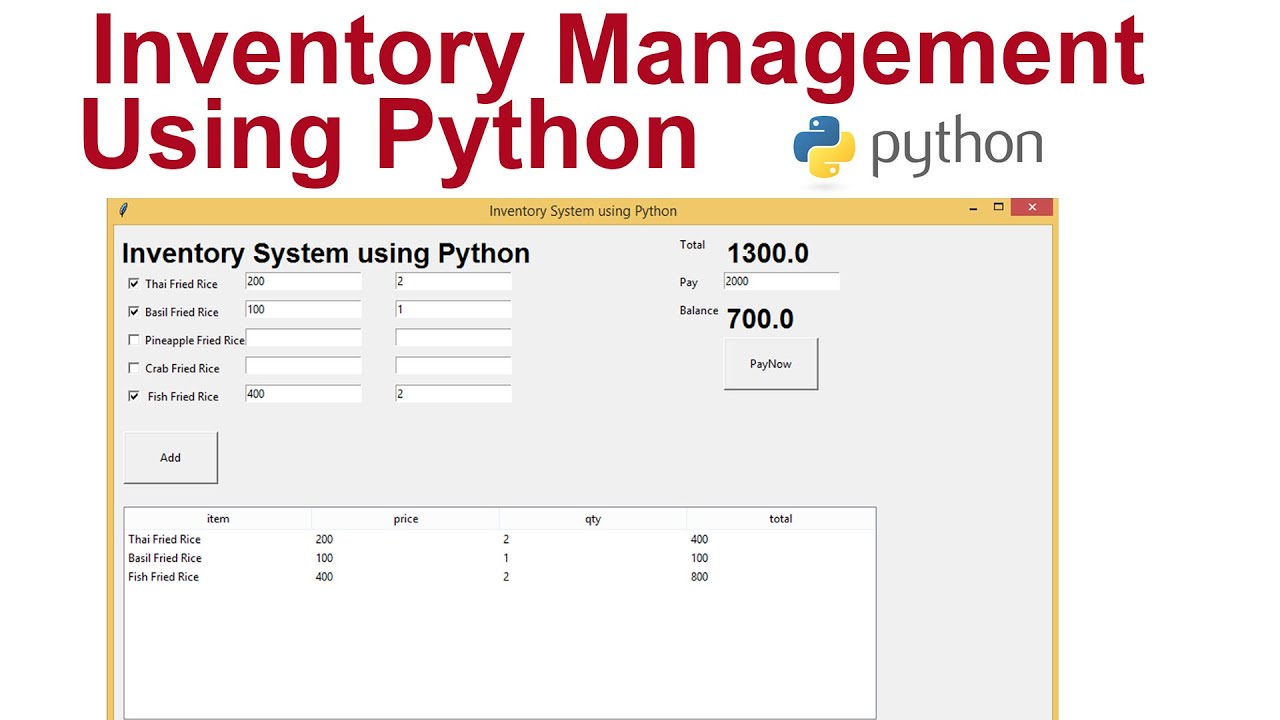
Inventory management software helps businesses track, manage, and optimize their inventory. It ensures that businesses have the right amount of stock at the right time. This software can be a game-changer for businesses of all sizes.
What Is Inventory Management Software?
Inventory management software is a tool that automates the process of tracking inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries. It helps in managing stock, preventing overstock and stockouts.
Here are some key features of inventory management software:
- Inventory Tracking: Monitors stock levels in real-time.
- Order Management: Manages customer orders and purchase orders.
- Sales Analysis: Provides sales data and trends.
- Supplier Management: Keeps track of suppliers and their performance.
- Reporting: Generates reports on inventory status and performance.
Importance Of Inventory Management Software For Businesses
Effective inventory management software is crucial for business success. Here are some reasons why:
- Cost Savings: Reduces the costs associated with overstock and stockouts.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlines the inventory management process.
- Better Decision Making: Provides accurate data for informed decisions.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensures products are available when customers need them.
- Time Savings: Automates tasks, saving valuable time.
Overall, inventory management software is essential for maintaining optimal stock levels, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Setting Up Your Python Development Environment
Before building your inventory management software in Python, you need to set up your development environment. This process involves installing Python and necessary packages and setting up a virtual environment. Following these steps ensures a smooth development experience.
Installing Python And Necessary Packages
First, install Python on your system. Visit the official Python website to download the latest version. Follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
After installing Python, you need to install essential packages. Use the following command to install pip, Python’s package installer:
pip install --upgrade pipNext, install the necessary packages for your project. Common packages for inventory management software include:
- Flask – for creating a web application
- SQLAlchemy – for database management
- Pandas – for data manipulation
Install these packages using pip:
pip install Flask SQLAlchemy pandasSetting Up A Virtual Environment
A virtual environment helps manage dependencies and avoid conflicts between projects. To create a virtual environment, use the following command:
python -m venv myenvReplace myenv with your preferred environment name. Activate the virtual environment using:
- Windows:
myenv\Scripts\activate - Mac/Linux:
source myenv/bin/activate
Once activated, your terminal prompt will change to indicate the active virtual environment. Install the necessary packages within this environment to ensure they are isolated from your global Python installation.
Deactivate the virtual environment using:
deactivateSetting up a virtual environment keeps your project organized and manageable. It also ensures that dependencies are consistent across different development and production environments.
Designing The Software Architecture
Creating effective inventory management software in Python requires a solid architectural design. The design phase is crucial as it sets the foundation for the software’s functionality and scalability. Let’s explore the key steps involved in designing the software architecture.
Defining Software Requirements And Specifications
The first step in designing inventory management software is to clearly define the requirements and specifications. This involves understanding what the software needs to achieve and how it will operate.
- Inventory Tracking: The software should track items in stock, monitor stock levels, and update quantities in real-time.
- Order Management: It should manage purchase orders, sales orders, and keep a record of transactions.
- Reporting: Generate reports on inventory status, stock movement, and sales performance.
- User Access: Implement different user roles and permissions for secure access.
Defining these specifications helps in creating a clear roadmap for development and ensures that all necessary features are included from the start.
Choosing A Database: Sql Vs Nosql
Selecting the right database is another critical decision. It impacts how data is stored, retrieved, and managed. Here, we’ll compare SQL and NoSQL databases to help you make an informed choice.
| Aspect | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Relational (tables) | Non-relational (documents, key-value pairs) |
| Schema | Fixed schema | Dynamic schema |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling | Horizontal scaling |
| Use Case | Structured data, complex queries | Unstructured data, flexible data models |
SQL databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL are ideal for applications requiring complex queries and data integrity. They use a fixed schema and are suitable for structured data.
NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra are better for flexible data models and unstructured data. They allow horizontal scaling and are suitable for applications with evolving data requirements.
Choose the database that aligns with your project’s needs and scalability requirements.
Creating The Database Schema
Creating a robust database schema is essential for effective inventory management software. In Python, a well-structured database ensures smooth data operations and integrity. We’ll focus on designing tables for products, suppliers, and inventory. We’ll also cover implementing relationships between these tables.
Designing Tables For Products, Suppliers, And Inventory
Begin by designing tables for products, suppliers, and inventory. Each table should have unique columns relevant to its entity.
| Table Name | Columns |
|---|---|
| Products |
|
| Suppliers |
|
| Inventory |
|
Implementing Relationships Between Tables
Implementing relationships between tables is crucial for data integrity. Establish foreign keys to connect related tables.
- Products Table: Contains unique product details.
- Suppliers Table: Stores supplier information.
- Inventory Table: Links products and suppliers, showing stock levels and additions.
Use SQLAlchemy for defining relationships in Python. Below is a sample code snippet:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String, ForeignKey, Date
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
Base = declarative_base()
class Product(Base):
__tablename__ = 'products'
product_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
product_name = Column(String)
category = Column(String)
price = Column(Integer)
quantity = Column(Integer)
inventory = relationship('Inventory', back_populates='product')
class Supplier(Base):
__tablename__ = 'suppliers'
supplier_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
supplier_name = Column(String)
contact_info = Column(String)
inventory = relationship('Inventory', back_populates='supplier')
class Inventory(Base):
__tablename__ = 'inventory'
inventory_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
product_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('products.product_id'))
supplier_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('suppliers.supplier_id'))
quantity = Column(Integer)
date_added = Column(Date)
product = relationship('Product', back_populates='inventory')
supplier = relationship('Supplier', back_populates='inventory')
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///inventory.db')
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
Each class represents a table, and relationships are defined using the relationship function. This setup ensures data consistency across the database.
By designing the tables and implementing relationships correctly, your inventory management software will have a strong foundation. This approach allows for efficient data retrieval and manipulation, ensuring smooth operations.
Building The Backend With Python
Creating a robust backend is crucial for any inventory management software. Python, with its simplicity and powerful libraries, makes this task easier. This section will guide you through connecting Python to the database and creating CRUD operations for inventory management.
Connecting Python To The Database
To begin, select a database system. Popular choices include MySQL, SQLite, and PostgreSQL. Install the necessary Python library to connect to your database:
- For MySQL:
pip install mysql-connector-python - For SQLite:
pip install sqlite3 - For PostgreSQL:
pip install psycopg2
Next, establish a connection to your database. Here is an example using SQLite:
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('inventory.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
Create the necessary tables for your inventory management software:
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE inventory (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
price REAL
)
''')
conn.commit()
Creating Crud Operations For Inventory Management
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete. These operations are essential for managing inventory data.
Create Operation
To add new items to the inventory:
def add_item(name, quantity, price):
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity, price)
VALUES (?, ?, ?)
''', (name, quantity, price))
conn.commit()
Read Operation
To retrieve and view inventory items:
def get_items():
cursor.execute('SELECT FROM inventory')
items = cursor.fetchall()
for item in items:
print(item)
Update Operation
To modify existing inventory items:
def update_item(id, name, quantity, price):
cursor.execute('''
UPDATE inventory
SET name = ?, quantity = ?, price = ?
WHERE id = ?
''', (name, quantity, price, id))
conn.commit()
Delete Operation
To remove items from the inventory:
def delete_item(id):
cursor.execute('DELETE FROM inventory WHERE id = ?', (id,))
conn.commit()
These CRUD operations enable efficient management of your inventory data. Implement them to ensure your inventory remains accurate and up-to-date.
Developing The User Interface
Creating an effective user interface (UI) is crucial in inventory management software. A well-designed UI ensures users can navigate the system effortlessly. Below, we will discuss the various aspects of developing the UI for your Python-based inventory management software.
Choosing A Framework For The Frontend (tkinter, Flask, Django)
Choosing the right framework for your UI is essential. Python offers several options:
| Framework | Best For | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Tkinter | Simple desktop applications | Easy to use, built into Python, suitable for basic UIs |
| Flask | Web-based applications | Lightweight, flexible, great for small web apps |
| Django | Complex web applications | Feature-rich, includes admin interface, scalable |
Each framework has its strengths. Tkinter is ideal for desktop applications, while Flask and Django are better suited for web applications.
Designing Forms And Views For Managing Inventory
Designing forms and views is a critical part of the UI. Here are some key components to consider:
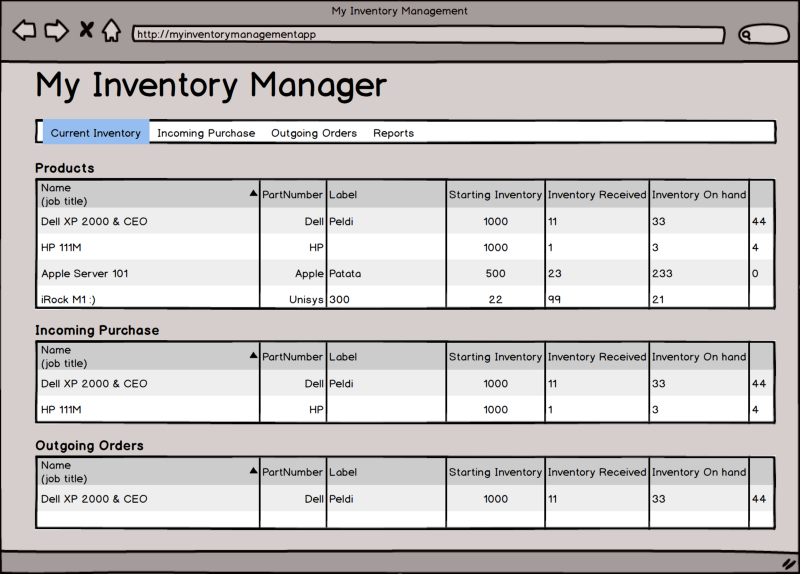
- Inventory List View: This view displays all inventory items. It should include columns for item name, quantity, price, and other relevant details.
- Add/Edit Item Form: This form allows users to add new items or edit existing ones. It should include fields for item name, quantity, price, and description.
- Search Functionality: Implementing a search bar will help users quickly find specific inventory items.
Below is an example of an inventory list view implemented using Tkinter:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
def create_inventory_view(root):
columns = ('Item Name', 'Quantity', 'Price')
tree = ttk.Treeview(root, columns=columns, show='headings')
tree.heading('Item Name', text='Item Name')
tree.heading('Quantity', text='Quantity')
tree.heading('Price', text='Price')
tree.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky='nsew')
# Example data
inventory = [
('Apples', 50, '$1.00'),
('Bananas', 30, '$0.50'),
('Cherries', 20, '$2.00')
]
for item in inventory:
tree.insert('', tk.END, values=item)
root = tk.Tk()
create_inventory_view(root)
root.mainloop()
This example demonstrates how to create a simple inventory list view. It displays item names, quantities, and prices. Customize it as needed for your specific application.
Implementing Inventory Management Features
Creating an inventory management system in Python requires implementing key features that ensure efficient tracking and management of products. In this section, we will cover essential functionalities such as adding products and suppliers, tracking inventory levels, and generating reports and analytics. Each feature is crucial for maintaining an organized inventory system.
Adding Products And Suppliers
To start, you need to create a way to add products and suppliers to your inventory system. This involves setting up a database to store product details and supplier information.
# Example code to add products and suppliers
import sqlite3
# Connect to database
conn = sqlite3.connect('inventory.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Create tables for products and suppliers
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
supplier_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (supplier_id) REFERENCES suppliers (id)
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS suppliers (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
contact TEXT
)
''')
# Function to add product
def add_product(name, quantity, supplier_id):
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO products (name, quantity, supplier_id)
VALUES (?, ?, ?)
''', (name, quantity, supplier_id))
conn.commit()
# Function to add supplier
def add_supplier(name, contact):
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO suppliers (name, contact)
VALUES (?, ?)
''', (name, contact))
conn.commit()
In this code, we create tables for products and suppliers. The add_product and add_supplier functions allow you to add new entries to these tables.
Tracking Inventory Levels
Tracking inventory levels is essential for ensuring that you always have the right amount of stock. You can achieve this by updating the quantity of products when items are added or removed.
# Function to update product quantity
def update_product_quantity(product_id, quantity):
cursor.execute('''
UPDATE products
SET quantity = ?
WHERE id = ?
''', (quantity, product_id))
conn.commit()
# Function to get product quantity
def get_product_quantity(product_id):
cursor.execute('''
SELECT quantity
FROM products
WHERE id = ?
''', (product_id,))
return cursor.fetchone()[0]
Use the update_product_quantity function to change the quantity of a product. The get_product_quantity function retrieves the current quantity of a product.
Generating Reports And Analytics
Generating reports and analytics helps in making informed decisions about inventory management. You can create functions to generate summaries of stock levels and track inventory trends.
# Function to generate inventory report
def generate_inventory_report():
cursor.execute('''
SELECT p.name, p.quantity, s.name
FROM products p
JOIN suppliers s ON p.supplier_id = s.id
''')
report = cursor.fetchall()
return report
# Function to display inventory report
def display_inventory_report():
report = generate_inventory_report()
print(f"{'Product':<20}{'Quantity':<10}{'Supplier':<20}")
print("-" 50)
for row in report:
print(f"{row[0]:<20}{row[1]:<10}{row[2]:<20}")
# Generate and display the inventory report
display_inventory_report()
The generate_inventory_report function retrieves product details and their suppliers. The display_inventory_report function formats and prints this information.
These features ensure a well-rounded inventory management system. By incorporating these functionalities, you can streamline the process of managing products, tracking inventory levels, and generating insightful reports.
Testing And Debugging The Software
Testing and debugging are essential steps in developing reliable inventory management software in Python. These processes ensure the software functions correctly and efficiently. Thorough testing and debugging can save time and prevent future issues. Below, we will discuss writing unit tests for backend functions and debugging common issues in inventory management systems.
Writing Unit Tests For Backend Functions
Writing unit tests is crucial for verifying that individual parts of the code work as expected. In Python, you can use the unittest module to create tests. Unit tests help identify bugs early and make the code more maintainable.
import unittest
from inventory_management import add_item, remove_item
class TestInventoryFunctions(unittest.TestCase):
def test_add_item(self):
inventory = {}
add_item(inventory, 'item1', 10)
self.assertEqual(inventory['item1'], 10)
def test_remove_item(self):
inventory = {'item1': 10}
remove_item(inventory, 'item1', 5)
self.assertEqual(inventory['item1'], 5)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
The code above tests the add_item and remove_item functions. It verifies that items are added and removed correctly in the inventory.
Debugging Common Issues In Inventory Management Systems
Debugging is the process of identifying and fixing bugs in the software. Common issues in inventory management systems include incorrect item counts, synchronization problems, and database errors.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Item Count | Logic errors in add/remove functions | Review and test the functions for accuracy |
| Synchronization Problems | Concurrency issues | Implement locks or use atomic operations |
| Database Errors | Invalid queries or connection issues | Check query syntax and connection settings |
Using a debugger, like pdb in Python, can help trace the code execution and identify where the issues occur. Place breakpoints in the code to inspect variables and flow.
import pdb
def add_item(inventory, item, quantity):
pdb.set_trace() # Breakpoint
if item in inventory:
inventory[item] += quantity
else:
inventory[item] = quantity
This example shows how to use the pdb.set_trace() function to pause the program and inspect the state of variables at that point. This can greatly aid in finding and fixing bugs.
Deploying The Application
Once you have developed your inventory management software in Python, the next step is to deploy it. This process involves preparing the application for deployment, choosing a hosting service, and ensuring everything runs smoothly. Below, we will discuss these steps in detail to help you get your application live and accessible to users.
Preparing The Application For Deployment
Before deploying your inventory management software, you need to prepare it properly. Start by ensuring that all dependencies are included and that your code is clean and optimized. Here are some steps to follow:
- Clean the Code: Remove any unnecessary files and comments.
- Package Dependencies: Use tools like
pipto manage your project dependencies. Create a requirements file usingpip freeze > requirements.txt. - Environment Variables: Use environment variables for sensitive information like database credentials and API keys.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to ensure the application is bug-free.
These steps will help ensure that your application is ready for a smooth deployment process.
Choosing A Hosting Service
Choosing the right hosting service is crucial for the performance and reliability of your application. Here are some factors to consider:
| Hosting Service | Features |
|---|---|
| Heroku | Easy to use, supports Python, free tier available. |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Highly scalable, comprehensive services, pay-as-you-go pricing. |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Robust infrastructure, excellent support for Python applications. |
| DigitalOcean | Cost-effective, simple interface, good for smaller projects. |
Consider the needs of your application, such as scalability, cost, and ease of use, when choosing a hosting service. Each option has its strengths, so choose one that aligns with your project’s requirements.
By carefully preparing your application and selecting the right hosting service, you can ensure a successful deployment of your inventory management software, making it accessible and functional for your users.
Credit: www.freecodecamp.org
Maintaining And Updating The Software
Maintaining and updating inventory management software is crucial. It ensures the system operates smoothly and meets evolving needs. Regular maintenance tasks and adding new features are key aspects of this process.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance keeps the software running efficiently. Some important tasks include:
- Database Management: Regularly clean and optimize the database.
- Backup: Create regular backups to prevent data loss.
- Security Updates: Apply security patches to safeguard data.
- Bug Fixes: Identify and fix bugs promptly.
These tasks ensure the software remains reliable and secure.
Adding New Features And Enhancements
Adding new features and enhancements keeps the software relevant. Consider the following steps:
- Identify Needs: Gather feedback from users to identify new requirements.
- Design: Plan the new features ensuring they integrate seamlessly.
- Development: Use Python to develop and test new features.
- Deployment: Deploy updates without disrupting the existing system.
Enhancements can include advanced reporting, integration with other systems, and improved user interface.
Regular updates ensure the software evolves with user needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Inventory Management Software?
Inventory management software helps businesses track, manage, and control stock levels. It ensures efficient inventory handling.
Why Use Python For Inventory Management Software?
Python is versatile, easy to learn, and has extensive libraries. These factors make it ideal for developing inventory management software.
How To Start Creating Inventory Software In Python?
Start by planning features and creating a database schema. Use Python libraries like Django or Flask for development.
What Libraries Are Useful For Inventory Management In Python?
Libraries like Pandas, SQLAlchemy, and Django are useful. They help with data handling and web development.
Conclusion
Creating inventory management software in Python can seem challenging. Yet, with the right steps, it becomes manageable. Start small and build on each feature. Remember to test your code regularly. This ensures your software works smoothly. For those looking to simplify scheduling, consider using TidyCal. It offers customizable booking pages, calendar integrations, and automation. Visit the TidyCal page here for more details. Happy coding, and may your project succeed!











